Social Determinants of health (SDH) are the conditions in which people born, grow, live, work and age.
- SDH are the social factors that largely determine the health and well-being of an individual as social factors are closely related for creating health risks and outcomes.
- These are the conditions which heavily influence the health that we achieve.
- SDH also refers to the bigger set of forces that shape the conditions of daily life of an individual. These forces can be social norms, culture, social practices, economic policies, developmental agendas along with political systems of any state/nation
- These social and economic factors/conditions have effect on our daily life and also determines our risk of suffering from disease, the actions that we can take to prevent the disease and one’s capacity to treat these diseases once it occurs
- Social determinants are considered as the root cause of our health and disease. Often times it is also known as the cause of the cause.
- SDH are shaped by the division and allocation of money, power and resources of the community/nation
- As social determinants of health includes multiple factors from physical factors, social factors, environmental factors, political factors etc, SDH is itself very complex, interrelated, overlapping and integrated
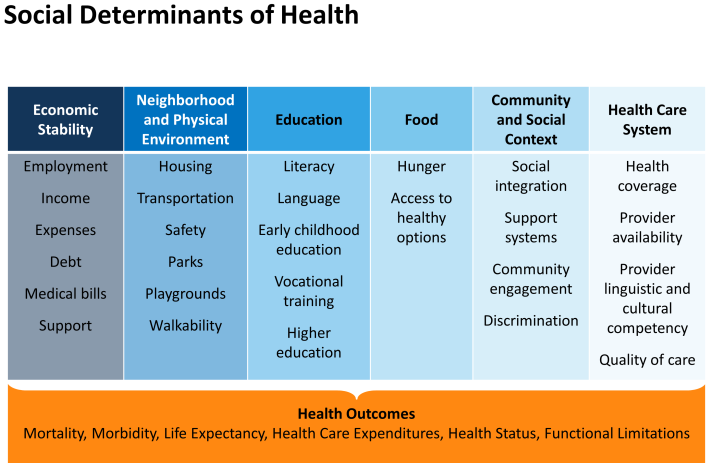
- SDH also has influences the health behavior of an individual.
- Good SDH creates good health and poor SDH like poor sanitation, low income, sub-standard education, unstable housing and job, dirty food and water etc creates bad/poor health of an individual. Thus, information and knowledge about SDH helps to improve the health of an individual.
- Example of SDH affecting health: poor education and income of a person leads to compromised living standard which ultimately leads to poor health (poor sanitation related diseases, nutritional deficiencies etc.), poverty and low income reduces access to better health services and health care.
- Furthermore, there are ten key determinants which influence health outcomes (‘Solid Facts’ by Michael Marmot and Richard Wilkinson). They are:
- Social gradient (extent of equity or the difference in wealth and opportunity between those with the most and those with the least)
- Early life
- Stress
- Social exclusion
- Working conditions
- Unemployment
- Social support
- Addiction
- Healthy food
- Transport
- Apart from being responsible for good/bad health, SDH is also one of the major factors which are responsible for health inequities among and between the countries. Therefore, health inequities and SDH are considered as a critical component for achieving Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) and Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
- At present, even World Health Organization (WHO) has kept SDH as one of its core functions for reducing health inequities and improving the health of all the people.
- WHO has established a Commission on Social Determinants of Health (CSDH) in 2005. The commission prepared a report for addressing health equity through the action of social determinants of health. There are three overarching recommendations/principles of action given by the commission on their report which are:
- Improve daily living conditions: It includes-
- Equity from the start
- Healthy places healthy people
- Fair employment and decent work
- Social protection across the life course
- Universal Health Care
- Tackle the inequitable distribution of money, power and resources: It includes
- Health equity in all policies, systems and programs
- Fair financing
- Market responsibility
- Gender equity
- Political empowerment- inclusion and voice
- Good global governance
- Measure and understand the problem and assess the impact of action
- Improve daily living conditions: It includes-
- WHO has its own WHO SDH unit whose function is to help, support, guide and strengthen the capacities of the countries/member states to develop, implement, monitor and evaluate programs to promote health equity
- Thus, social determinants of health are one of the major determinants for creating a good health and reducing the existing unfair and avoidable inequity between and among the people living in different parts of the world